Strophidon sathete
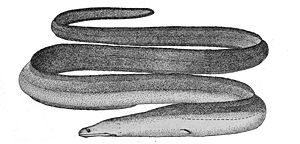 Il·lustració del 1911 | |
| Estat de conservació | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Risc mínim | |
| UICN | 195817 |
| Taxonomia | |
| Superregne | Holozoa |
| Regne | Animalia |
| Fílum | Chordata |
| Classe | Actinopteri |
| Ordre | Anguilliformes |
| Família | Muraenidae |
| Gènere | Strophidon |
| Espècie | Strophidon sathete Hamilton, 1822 |
| Nomenclatura | |
| Sinònims |
|
Strophidon sathete és una espècie de peix marí pertanyent a la família dels murènids i l'única del gènere Strophidon.[4][5]
Etimologia
[modifica]Strophidon prové dels mots grecs strophos (retorçat) i odous (dents).[6]
Descripció
[modifica]Fa 4 m de llargària màxima[7] (encara que la seua mida més comuna és de 70 cm)[7] i és de color gris marronós a la part superior i més clar per sota.[8] Cos moderadament allargat, cilíndric per davant i comprimit al llarg de la cua. Ulls petits. Boca molt gran i estesa fins més enllà dels ulls. Dents petites, biserials, esmolades i més grans al davant i la filera interior. Aleta dorsal inserida al cap abans de l'obertura branquial. Absència d'escates. 183-196 vèrtebres.[9] Línia lateral contínua.[10]
Alimentació
[modifica]Menja principalment una gran varietat de peixets i crustacis.[11] El seu nivell tròfic és de 3,98.[12]
Hàbitat i distribució geogràfica
[modifica]És un peix marí i d'aigües dolces i salabroses, associat als esculls (fins als 15 m de fondària),[13] amfídrom[14] i de clima tropical (23 °C-28 °C;[15] 30°N-23°S),[11] el qual viu a la conca Indo-Pacífica: els fons oceànics fangosos,[16] els estuaris,[17] els rius[17] i les badies interiors[18] des del mar Roig[19] i l'Àfrica oriental fins al Pacífic occidental, incloent-hi Somàlia,[20] Kenya,[21] Tanzània,[22][23] Moçambic,[24] Sud-àfrica,[25] Madagascar,[26] l'illa de Reunió,[27] Maurici,[28][29] el corrent Agulhas,[30] les illes Maldives,[31] l'Índia -com ara, les illes Andaman[32] i la llacuna Chilka[33]-, la badia de Bengala,[34] les illes Filipines -com ara, la badia de Sogod[35]-, el mar de la Xina Meridional,[36] el mar de la Xina Oriental,[37] el Vietnam,[38] Hong Kong,[39] Taiwan[16] -incloent-hi el riu Erren[40]-, la mar Groga,[16] el corrent de Kuroshio,[41] el Japó[42] -incloent-hi les illes Ryukyu[43]-, Indonèsia,[44][45] Papua Nova Guinea,[46] Austràlia,[47] el mar del Corall,[17] la Gran Barrera de Corall,[17][48] Nova Caledònia,[49][50] Vanuatu,[51] la República de Palau,[13] Fiji[13] i Guam.[13][3][52]
Observacions
[modifica]És de costums solitaris,[53] el seu índex de vulnerabilitat és molt alt (80 de 100),[54] es comercialitza fresc a nivell local[7] i és conegut per estendre's verticalment des del seu cau amb el cap en posició horitzontal i pujant i baixant seguint el vaivé de la marea.[55]
Referències
[modifica]- ↑ Bleeker, P., 1854. Ichthyologische waarnemingen, gedaan op verschillende reizen in de residentie Banten. Natuurkundig Tijdschrift voor Nederlandsch Indië, vol. 7: 309-326. [1]
- ↑ Tanaka, S., 1918. Two new species of Japanese fishes. Dobutsugaku Zasshi = Zoological Magazine Tokyo, vol. 30 (núm. 352): 51-52.
- ↑ 3,0 3,1 Catalogue of Life Arxivat 2014-10-23 a Wayback Machine. (anglès)
- ↑ The Taxonomicon (anglès)
- ↑ Encyclopedia of Life (anglès)
- ↑ Romero, P., 2002. An etymological dictionary of taxonomy. Madrid, l'Estat espanyol.
- ↑ 7,0 7,1 7,2 Castle, P. H. J., 1984. Muraenidae. A: W. Fischer i G. Bianchi (eds.). FAO species identification sheets for fishery purposes. Western Indian Ocean (Fishing Area 51). Vol. 1. FAO, Roma.
- ↑ Castle, P. H. J. i J. E. McCosker, 1986. Muraenidae. P. 165-176. A: M. M. Smith i P. C. Heemstra (eds.). Smiths' sea fishes. Springer-Verlag, Berlín. Pàg. 174.
- ↑ Talwar, P.K. i A.G. Jhingran, 1991. Inland fishes of India and adjacent countries. Vol 1. A.A. Balkema, Rotterdam. 541 p. Pàg. 79.
- ↑ Morphology Data of Strophidon sathete - FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ 11,0 11,1 FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ Sea Around Us (anglès)
- ↑ 13,0 13,1 13,2 13,3 Myers, R. F., 1991. Micronesian reef fishes. Segona edició. Coral Graphics, Barrigada, Guam. 298 p. Pàg. 48.
- ↑ Riede, K., 2004. Global register of migratory species - from global to regional scales. Final Report of the R&D-Projekt 808 05 081. Federal Agency for Nature Conservation, Bonn, Alemanya. 329 p.
- ↑ Baensch, H.A. i R. Riehl, 1997. Aquarien Atlas, Band 5. Mergus Verlag, Melle (Baixa Saxònia), Alemanya. 1148 p.
- ↑ 16,0 16,1 16,2 Chen, H.-M., K.-T. Shao i C. T. Chen, 1994. A review of the muraenid eels (Family Muraenidae) from Taiwan with descriptions of twelve new records. Zool. Stud. 33(1):44-64. Pàg. 54.
- ↑ 17,0 17,1 17,2 17,3 Randall, J. E., G. R. Allen i R. C. Steene, 1990. Fishes of the Great Barrier Reef and Coral Sea. University of Hawaii Press, Honolulu, Hawaii. 506 p. Pàg. 42.
- ↑ Myers, R. F., 1999. Micronesian reef fishes: a comprehensive guide to the coral reef fishes of Micronesia. 3a edició revisada i ampliada. Coral Graphics, Barrigada, Guam. 330 p. Pàg. 51.
- ↑ Golani, D. i S. V. Bogorodsky, 2010. The fishes of the Red Sea - reappraisal and updated checklist. Zootaxa 2463:1-135. Pàg. 11.
- ↑ Sommer, C., W. Schneider i J.-M. Poutiers, 1996. FAO species identification field guide for fishery purposes. The living marine resources of Somalia. FAO, Roma. 376 p. Pàg. 139. [2]
- ↑ List of Marine Fishes for Kenya - FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ Bianchi, G., 1985. FAO species identification sheets for fishery purposes. Field guide to the commercial marine and brackish-water species of Tanzania. Prepared and published with the support of TCP/URT/4406 and FAO (FIRM) Regular Programme. FAO, Roma. 199 p. Pàg. 14.
- ↑ List of Marine Fishes reported from Tanzania - FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ List of Marine Fishes for Mozambique - FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ List of Marine Fishes reported from South Africa - FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ List of Marine Fishes reported from Madagascar - FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ Letourneur, Y., P. Chabanet, P. Durville, M. Taquet, E. Teissier, M. Parmentier, J.-C. Quéro i K. Pothin, 2004. An updated checklist of the marine fish fauna of Reunion Island, south-western Indian Ocean. Cybium 28(3):199-216. Pàg. 208. [3]
- ↑ Baissac, J. de B., 1990. SWIOP/WP/54 - Checklist of the marine fishes of Mauritius. RAF/87/008/WP/54/90 Regional Project for the Development & Management of Fisheries in the Southwest Indian Ocean. [4] Arxivat 2015-09-24 a Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Cornic, A., 1987. Poissons de l'Ile Maurice. Editions de l'Océan Indien, Stanley Rose Hill, Maurici. 335 p. Pàg. 104.
- ↑ Fischer, W., I. Sousa, C. Silva, A. de Freitas, J. M. Poutiers, W. Schneider, T. C. Borges, J.P. Feral i A. Massinga, 1990. Fichas FAO de identificaçao de espécies para actividades de pesca. Guia de campo das espécies comerciais marinhas e de águas salobras de Moçambique. Publicaçao preparada em collaboraçao com o Instituto de Investigaçao Pesquiera de Moçambique, com financiamento do Projecto PNUD/FAO MOZ/86/030 e de NORAD. Roma, FAO. 424 p. Pàg. 160.
- ↑ Randall, J. E. i C. Anderson, 1993. Annotated checklist of the epipelagic and shore fishes of the Maldives Islands. Ichthyol. Bull. of the J. L. B. Smith Inst. of Ichthyol. 59:47. Pàg. 7.
- ↑ Rajan, P. T., C. R. Sreeraj i T. Immanuel, 2011. Fish fauna of coral reef, mangrove, freshwater, offshore and seagrass beds of Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Zoological Survey of India, Andaman and Nicobar Regional Centre, Haddo, Port Blair.
- ↑ Rao, K. V. R., 1995. Pisces. P. 483-506. A: Fauna of Chilka Lake. Wetland Ecosystem Series 1. Zool. Surv. India. 673 p. Pàg. 485.
- ↑ Kapoor, D., R. Dayal i A.G. Ponniah, 2002. Fish biodiversity of India. National Bureau of Fish Genetic Resources, Lucknow, l'Índia. 775 p. Pàg. 61.
- ↑ Calumpong, H. P., L. J. Raymundo i E. P. Solis-Duran (eds.), 1994. Resource and ecological assessment of of Sogod Bay, Leyte, Philippines - Final Report Vol.1 Fisheries Assessment. Siliman University Marine Laboratory. Pàg. 37.
- ↑ Randall, J.E. i K. K. P. Lim (eds.), 2000. A checklist of the fishes of the South China Sea. Raffles Bull. Zool. Suppl. (8): 569-667. Pàg. 615. [5]
- ↑ Huang, Z., 2001. Marine species and their distribution in China's seas. p. 404-463. Vertebrata. Smithsonian Institution, Florida, Estats Units. 598 p. Pàg. 417.
- ↑ Nguyen, H. P. i N. T. Nguyen, 1994. Checklist of marine fishes in Vietnam. Vol. 2. Osteichthyes, from Elopiformes to Mugiliformes. Science and Technics Publishing House, el Vietnam. Pàg. 96.
- ↑ Ni, I.-H. i K.-Y. Kwok, 1999. Marine fish fauna in Hong Kong waters. Zool. Stud. 38(2):130-152. Pàg. 134. [6] Arxivat 2012-12-24 a Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Kuo, S.-R. i K.-T. Shao, 1999. Species composition of fish in the coastal zones of the Tsengwen estuary, with descriptions of five new records from Taiwan. Zool. Stud. 38(4):391-404. Pàg. 397.
- ↑ Masuda, H., K. Amaoka, C. Araga, T. Uyeno i T. Yoshino, 1984. The fishes of the Japanese Archipelago. Vol. 1. Tokai University Press, Tòquio, el Japó. 437 p. Pàg. 22.
- ↑ Masuda, H., C. Araga i T. Yoshino, 1975. Coastal fishes of southern Japan. Tokai University Press, Tòquio. 382 p. Pàg. 171.
- ↑ List of Marine Fishes reported from Ryukyu Islands - FishBase (anglès)
- ↑ Kottelat, M., A. J. Whitten, S. N. Kartikasari i S. Wirjoatmodjo, 1993. Freshwater fishes of Western Indonesia and Sulawesi. Periplus Editions, Hong Kong. 221 p.
- ↑ Allen, G. R. i M. Adrim, 2003. Coral reef fishes of Indonesia. Zool. Stud. 42(1):1-72. Pàg. 23.
- ↑ Kailola, P. J., 1987. The fishes of Papua New Guinea. A revised and annotated checklist. Vol. 1. Myxinidae to Synbranchidae. Research Bulletin No. 41. Department of Fisheries and Marine Resources, Port Moresby, Papua Nova Guinea. 194 p. Pàg. 45.
- ↑ Hoese, D. F., D. J. Bray, J. R. Paxton i G. R. Allen, 2006. Fishes. A: Beasley, O. L. i A. Wells (eds.). Zoological Catalogue of Australia. Vol. 35.2 Australia: ABRS & CSIRO Publishing, 1472 p. Pàg. 258.
- ↑ Hardy, J. D. Jr., 2003. Coral reef fish species. NOAA\National Oceanographic Data Center. NODC Coral Reef Data and Information Management System. Els Estats Units. 537 p. Pàg. 35.
- ↑ Thollot, P., 1996. Les poissons de mangrove du lagon sud-ouest de Nouvelle-Calédonie. ORSTOM Éditions, París. Pàg. 306.
- ↑ Kulbicki, M., G. Mou Tham, P. Thollot i L. Wantiez, 1993. Length-weight relationships of fish from the lagoon of New Caledonia. Naga ICLARM Q. 16(2-3):26-29.
- ↑ David, G., 1985. Pêche de subsistance et milieu naturel: les mangrove de Vanuatu et leur intérêt halieutique. Notes et documents d'océanographie. Mission ORSTOM de Port-Vila, 13:67 p. multigr.
- ↑ GBIF (anglès)
- ↑ Allen, G. R. i M. V. Erdmann, 2012. Reef fishes of the East Indies. Perth, Austràlia: Universitiy of Hawai'i Press, Volumes I-III. Tropical Reef Research. Pàg. 97.
- ↑ Cheung, W. W. L., T. J. Pitcher i D. Pauly, 2005. A fuzzy logic expert system to estimate intrinsic extinction vulnerabilities of marine fishes to fishing. Biol. Conserv. 124:97-111.
- ↑ Lieske, E. i R. Myers, 1994. Collins Pocket Guide. Coral reef fishes. Indo-Pacific & Caribbean including the Red Sea. Harper Collins Publishers, 400 p.
Bibliografia
[modifica]- Anònim, 1998. Base de dades de la col·lecció de peixos del Bernice P. Bishop Museum (BPBM). Bishop Museum, 1525 Bernice Street, Honolulu, Hawaii, els Estats Units.
- Anònim, 1999. Base de dades de la col·lecció de peixos del Museu d'Història Natural de Londres. Londres, la Gran Bretanya.
- Anònim, 2000. Base de dades de la col·lecció de peixos del Gulf Coast Research Laboratory (GCRL). The Gulf Coast Research Laboratory (GCRL), Ocean Springs, Mississipi, els Estats Units.
- Anònim, 2000. Base de dades de la col·lecció de peixos del J.L.B. Smith Institute of Ichthyology, Grahamstown, Sud-àfrica. J.L.B. Smith Institute of Ichthyology, Grahamstown, Sud-àfrica.
- Anònim, 2000. Col·lecció ictiològica del Museu Zoològic d'Hamburg (Zoologisches Museum Hamburg). Divisió d'Ictiologia i Herpetologia. Museu Zoològic d'Hamburg (ZMH).
- Divisió de Peixos de la Smithsonian Institution. Base de dades de la col·lecció de peixos del Museu Nacional d'Història Natural (en anglès). Smithsonian Institution, 2001.
- Anònim, 2003. Col·lecció de peixos del Museu Reial d'Ontario. Museu Reial d'Ontario.
- Böhlke, E. B. i D. G. Smith, 2002. Type catalogue of Indo-Pacific Muraenidae. Proceedings of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, vol. 152: 89-172.
- Eschmeyer, W.N., 1990. Catalog of the genera of recent fishes. California Academy of Sciences, San Francisco, els Estats Units. 697 p. ISBN 0940228238.
- IGFA, 2001. Base de dades de registres de pesca IGFA fins al 2001. IGFA, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, els Estats Units.
- Shiao, J. C., C. S. Tzeng, C. L. Leu i F. C. Chen, 1999. Enhancing the contrast and visibility of daily growth increments in fish otoliths etched by proteinase K buffer. J. Fish Biol. 54:302-309.
- Smith, D. G., 2012. A checklist of the moray eels of the world (Teleostei: Anguilliformes: Muraenidae). Zootaxa, núm. 3474: 1-64. [7]
- Wu, H.L., K.-T. Shao i C.F. Lai (eds.), 1999. Latin-Chinese dictionary of fishes names. The Sueichan Press, Taiwan.


